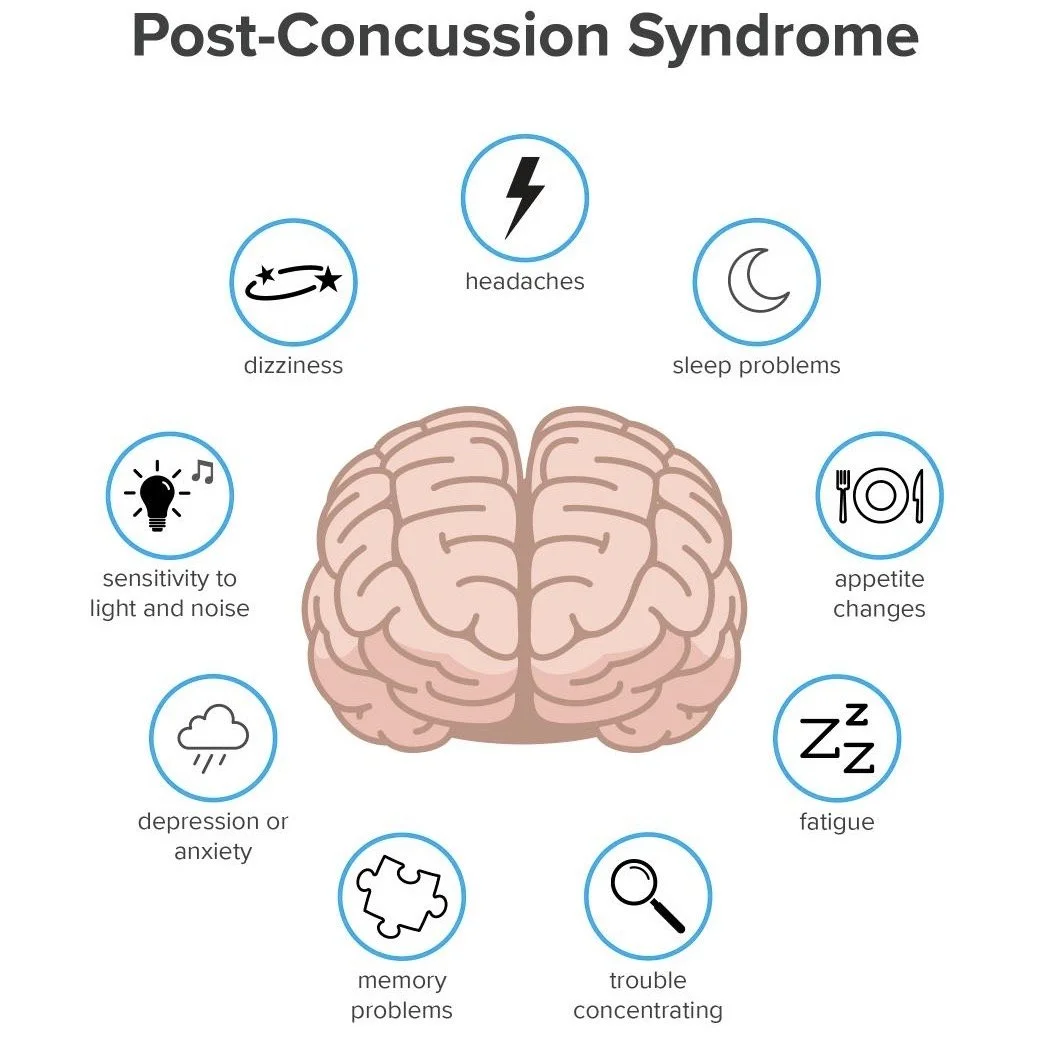
Concussion Recovery
A concussion is a brain injury caused by an impact to the head or body that affects how your brain functions. At ProPerformance, we take a functional approach to concussion and TBI diagnosis and rehabilitation. ProPerformance integrates advanced technology to assist in the diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of concussions. We offer a post-concussion recovery program for those who have sustained a head injury and are still experiencing symptoms. Our concussion care program includes a comprehensive exam followed by an individualized treatment plan.
How soon after a concussion should I come in for treatment? There is no time limit on when you can seek treatment following a concussion or head injury. Research has shown that the sooner you see a concussion specialist, the sooner you can recover. Following a thorough assessment, we will create an individualized treatment protocol, using the latest evidence-based therapies, to help manage concussion symptoms and restore function.
We use several modalities to evaluate and treat our concussion and TBI patients
Computerized Assessment of Postural Stability (CAPS®) is the gold standard in balance assessment technology. It uses a force plate that provides a detailed evaluation of a patient’s balance over time.
VisualEyes™ Videonystagmography (VNG) is an inferred video oculography assessmemt tool used to track eye movements in extreme detail. We use special infrared goggle technology to get an objective measurement of oculomotor function. Impaired eye movements have been identified as a common post-concussion problem and can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, headaches, difficulty reading or using a computer. Eye tracking problems can cause many corrective saccades, leading sufferers to feel “foggy” or fatigued when in a visually stimulating environment.
Interactive Metronome provides tailored training to improve motor sequencing, neural timing, cognition, and behavioral skills. To complement the in-office training that we do, we offer a home training program to further promote neuroplasticity and continue with rehabilitation.
Dynavision D2™ is the leading visual motor and neuro-cognitive rehabilitation device used for all stages of concussion management, better decision making and concentration under stress. The D2™ evaluates and trains visual acuity and cognitive processing while helping to improve reaction time, peripheral visual awareness, and functional mobility.
Erchonia Low-Level Laser is an FDA-approved low-level laser therapy (LLLT) to alter cellular functions and provide noticeable pain relief. LLLT has a photochemical effect that naturally reduces oxidative stress and increases the production of ATP, an energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. This innovative technology targets numerous conditions with no pain, no side effects, and no downtime. This is also known as cold laser therapy.
Repetitive Peripheral Somatosensory Stimulation (pontine stimulation) RPSS, also referred to as Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP) tests and/or stimulates the conduction of the nervous system and brain as part of treatment.
Neuro Sensorimotor Integrator or NSI, is designed for, and available only to Functional Neurologists. Using a 50 inch HD touch screen TV, the NSI is designed to offer a host of therapy procedures to a wide range of patients requiring visual or neuro-therapy following: TBI, Concussion, Whiplash, Neurological Disorders, Vestibular & Balance Disorders and Spinal Cord Injuries
EQ Brain Performance is a neurocognitive assessment that objectively measures functionality across a broad array of cognitive tasks that challenges the brain, with recall, short-term working memory, motor planning, recognition, spatial mapping, balance, executive functionality, reaction time, etc.
Saccadometry uses an infrared laser to observe eye motion following visual stimuli and compare it to expected norms. Saccadometry allows us to identify any visual latency or inaccuracy that could come as a result of trauma. Gaze stability and dynamic inaccuracies are often the foundation of post-concussion problems.
Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound provides rapid, noninvasive, real-time measures of cerebrovascular function. TCD can be used to measure flow velocity in the basal arteries of the brain to assess relative changes in flow, diagnose focal vascular stenosis, or to detect embolic signals within these arteries. TCD can also be used to assess the physiologic health of a particular vascular territory by measuring blood flow responses to changes in blood pressure (cerebral autoregulation), changes in end-tidal CO2 (cerebral vasoreactivity), or cognitive and motor activation (neurovascular coupling or functional hyperemia).